|
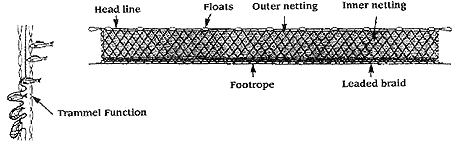
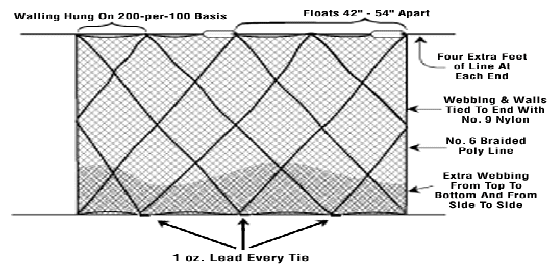
A trammel net consists of three layers of net. A slack,
small mesh, inner panel of netting is sandwiched between
two outer layers of netting, which are taught and have a
larger mesh size.
The inner panel may be made of twisted or
monofilament nylon, whilst the outer panels are generally
made of
twisted
nylon
filament.
Trammel
nets are
held
vertically
in the
water by
weights on
the bottom
(lead line),
and floats on the top (float line).
According to their design, ballasting and
buoyancy, these nets may be used to fish
near the surface, in midwater orat the bottom,
either in inland or marine waters.
Trammel nets are used to catch demersal,
benthic and pelagic species.
Both trammel and gill nets entangle fish in
three different ways. The fish may become
wedged, held by the mesh around the body;
gilled, caught by the gills; and tangled, held by teeth, spines or other protrusions without necessarily penetrating the mesh.
In addition, trammel nets also entangle fish in bags or pockets of netting.
This occurs when fish swim through one of the outer panels, hit the inner panel, and are carried through to the other outer panel, which creates a bag or pocket, thereby trapping the fish.
Although trammel nets are used extensively in European waters,
monitoring of these fisheries has been very limited.
However, from the data available, it would appear that, in
terms of catching fish, a trammel net is less selective than a
gill net, in terms of the size and species caught.
As a result, there are high levels of fish discards in trammel
net fisheries.
http://www.europarl.eu.int/stoa/publi/98-17-01/chap1_en.htm
These high levels of discards have a significant impact
on cetacean populations.
Evidence suggests that an increasing number of cetaceans are malnourished due to depleted fish stocks.
April - June 2001: when 43 cetaceans were post-mortemed in the UK, 10% were found to have died of starvation.
Tethys Report - Reeves, et al 2001 - pdf 425KB
|